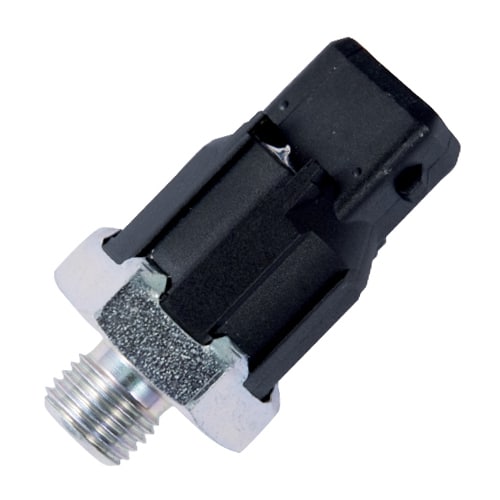
The knock sensor is located in the engine block so that it registers the knocking noise caused by the knocking effect and transforms it into an electrical signal. The control unit compares the signal with the stored specification values and intervenes to control the engine, fuel injection and ignition as necessary, before combustion reaches the knock limit.
Products
We have what you are looking for
Description
Technical data
Composition
Cause of failure
Mounting
Description
What is the knock sensor for?
Knock Sensors prevents from a harmful spontaneous ignition resulting in the knocking effect.
Theacyclic uncontrolled combustions results in a high temperature inside the cylinder. This phenomenon causes that, engine parts like pistons, valves or the cylinder head, are subjected to high stress.
Where is the knock sensor located?
The knock sensor is located in the engine block so that it registers the knocking noise caused by the knocking effect and transforms it into an electrical signal. The control unit compares the signal with the stored specification values and intervenes to control the engine, fuel injection and ignition as necessary, before combustion reaches the knock limit.
Technical data
Knock Sensors are differentiated by their Sensitivity (S). Sensitivity is the relationship between the voltage generated between its terminals and the acceleration to which it is being subjected. It is expressed in mVolts/g.
Knock Sensors of non-resonant type have the property to maintain its sensitivity almost constant throughout its whole range of reading.

· Within the wide range available can be found with or without discharge resistor.
All knock sensors are subjected to rigorous tests and tested in response to 100%.
- Working range (1…20 kHz)
- Sensitivity at 5 kHz (each sensor Own)
- Working temperature (-40ºC…140ºC)
- Range of Capacity (800…1400 pF)
- Main Resonance (> 25 kHz)
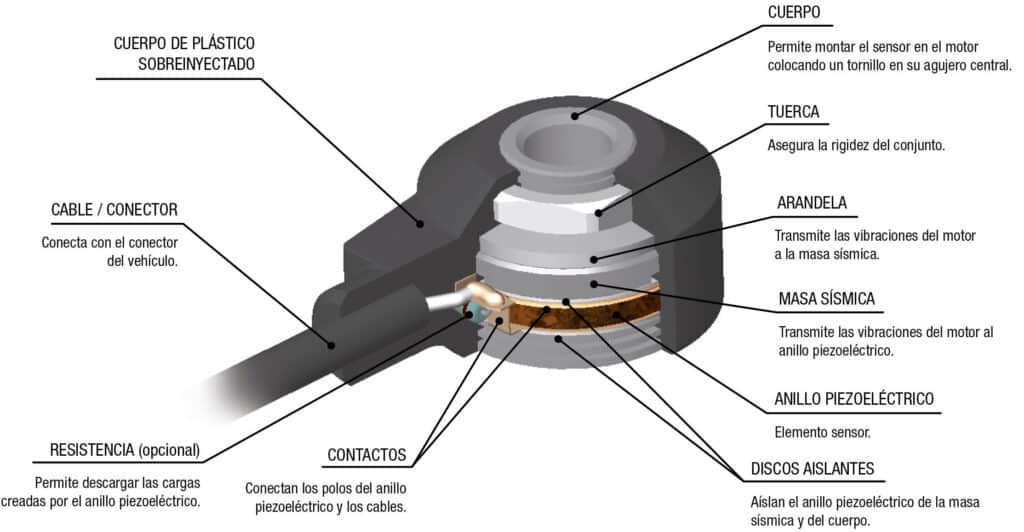
Composition
Inside the Knock Sensor there is a piezoelectric ring with a metal contact in each of their faces and perfectly isolated from the body and the seismic mass. The piezoelectric sensor is a ceramic ring which polarizes when exposed to an external electric field, so that, when subjected to compressive forces can generate a potential difference. The seismic mass is a metal ring perfectly calibrated to achieve the required sensitivity, so that when placed next to the sensor and compressed by a spring washer and a threaded nut (due to the inertial force) transmits the vibrations to the sensor element.
The sensor metal part (body) is responsible for transmitting the vibrations from the engine block, so that, before fitting it we need to ensure that the area is clean and in a good condition, otherwise it would not be possible to guarantee the proper functioning of the sensor.
Cause of failure
Knock sensor faults
The body Sensor, the connector and the cable should be checked, ensuring their good condition. Also check if the knock sensor body shows any crack, dents or impact that may have deteriorated it.
The sensor body, the connector and the cable should be checked to ensure that they are in good condition. Also check if the sensor body has any cracks, dents or knocks that could have damaged it.

- Cracks and breaks. Stresses caused by mechanical stress
- Deformations and dents. Overheated sensor
- Metal body corrosion. Wrong anchor to the block engine
- No signal. Cable breakage due to friction or excessive vibration; and internal sensor breakage due to mechanical or thermal stress
Mounting
Mounting the knock sensor
To ensure a proper torque reading the tightening torque should be 20 ± 5Nm. The sensor metal part must be in direct contact with the motor unit (without washers). In order to improve the vibrations transmission it is recommended to apply a thin silicone layer in the sensor base.
Associated documentation
DO YOU WANT MORE INFORMATION?
